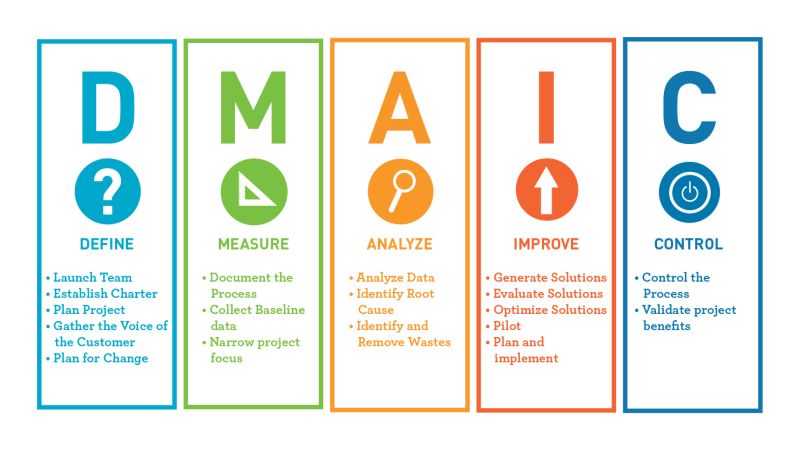
Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control (DMAIC) is a data-driven strategy used to improve processes.
It can be implemented as a standalone quality improvement procedure or as part of other process improvement initiatives (Six-Sigma etc).
DMAIC isn’t used as a quick fix – it’s best used on problems that are important, but not urgent.
Define

The business problem should be clearly articulated along with the goal, potential resources and estimated completion timeline. Facts should be clarified and all information ideally captured in a document using software like Notion on Roam Research.
Measure

In this phase, current and historical data is collected and a set of KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are put together. Targets are set and the KPIs are used to measure ongoing performance.
Analyse

An analysis is performed to identify and validate the root causes of the problem. Complex problems often have more than one root cause, therefore Mindmaps (one of my favourite tools) can be used here to make sure the process is fully analysed.
Improve

This stage is all about identifying, testing and implementing a solution to the problem. Any risks associated with the improvement action should be clearly communicated. Be careful not to dive into the “improve” stage before getting your processes and documentation in place – you want to be sure all bases are.
Control

Improvements should be monitored (against KPIs and other data points) to ensure continued and sustained success. An ongoing review process should be set, along with updating any internal documentation, business processes and relevant training material.
DMAIC is a data-driven approach to improvement. It isn’t used for quick fixes and best used on problems that are important, but not urgent.
