
1. Timeline
-
Past : Past will help to know the changes over the previous years.
-
Present: This is also called a Landing. Companies prepares the Landing by combining Actual + Forecast to know the expecting annual results.
-
Future: The short-term objective that organization use as part of its long-term plan
2. Building the Present is equally important as building the Future.
Many organizations do not give right focus on building Q4 projection while making
next year budgets.The projection plays an important role in preparing the budget for the next year. Too many companies fail to supplement the annual budget with forecasting/projection, Due to this, companies absorb lot of surprises of previous year in the current year budget.
Finance must play an important role to build the projection for building the better future.
While making projection, consider the following:
-
Projection should be accurate.
-
Comprehensive
-
Realistic
-
Does not hide mistakes
-
Transparent

3. Budgeting
Budgeting is Planning to develop the financial picture of business. It works as Management tool enable to start looking at the future. It’s a combined intelligence of an entire organization based on past and present performance. A Plan for spending and saving money. It is a static document and cannot be changed. It ensures that you will always have enough money for the things you need. Budget or spending plan will also keep you out of debt or help you work your way out of debt if you are currently in debt.
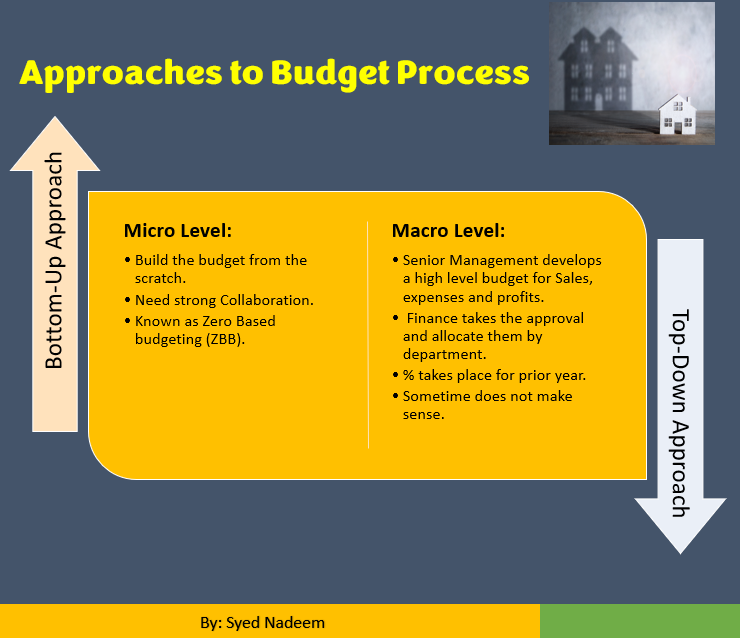
Approaches to Budget Process
4. Forecasting
-
Estimate of what business will actually achieve.
-
Often use as Short-term planning.
-
Want to know if there are some changes in the business.
-
It is based on historical data and business drivers and provide high-level overview.
-
Generally, forecast needs update on a regular basis.
-
It can be acceptable if we change forecast minimum quarterly or six monthly.
-
It helps to optimize the business depending on the change of various factors.
Why is Forecast becoming so important?
It helps organization to see a bigger and more accurate picture. This level of insight further enables your business to respond to market conditions faster, thereby making your organization more agile and competitive, inefficient tasks, allowing you to quickly anticipate and adapt to changing market conditions. It is dynamic and variances can be corrected anytime. Consider it honest forecast and more of it 70% of the employee can see how they affect the organization.
Why is Forecast becoming so important?
-
Use the right tool: Finance teams usually turn to Excel for forecasting. But that may not be sound business practice. The smarter, more strategic approach is to deploy an enterprise performance management (EPM) solution. Adopting BI and AI technologies can be the game changer and will turn your business data into a commercial advantage by making instantaneous optimized business decisions.
-
Establish the objective: As rolling forecasts are used to determine potential future outcomes, you’ll need to establish which areas of your plan need greater detail to be able to create forecasts.
-
Determine your forecast duration:Forecasting can be a little tricky. Questions around the duration of a forecast and whether you should account for additional months or forecast out by 2 years come to mind. Keep your forecast and business cycle aligned, but add a minimum of a quarter to your forecast.
5. Factor for Non-Financial Planning
-
Expand sales to the existing customers
-
Customer Satisfaction
-
Planning & Reporting System
-
Develop new product portfolio.
-
Adopt Latest Technology
-
Employee Training and Development
-
Change Management
-
Policies and Procedures
6. A Process to Initiate Financial Planning
Sales Budget
-
Need full market analysis and the experience.
-
High, Medium, Low (Seasonal changes)
-
External Variables
-
Government polices
-
Health of economyDemographic
-
Technology trends
-
Customers’ needs
-
Barriers of market entry
-
Seasonal change in demand
-
-
Internal Variables
-
Capacity
-
Collaboration and Teamwork
-
Alignment on common goal.
-
Launch of New products
-
Selling and Distribution Channels
-
Price Fluctuation
-
Market Demand and Research
-
Operating Cost Budget
-
Cost of product.
-
Human Resource Cost
-
Selling and Marketing Expenses
-
General and Administrative Expenses
-
Shared Cost Allocation.
Cash Budget
-
Plan for Inflow and Outflow to manage the cash position.
-
If customer is not able to pay on time, the company might not be able to pay the liabilities.
-
Consequently, Sales might decline.
-
The company start approaching loans from bank to secure the consequences expected to be happed by bad receivable position.
-
The Budget help management to identify the areas where they can cut down expenditure or get the financing from bank.
Capital Expenditure Budgets.
-
Evaluation of large project and finance those projects.
-
Also called investment appraisals.
-
Examples:
-
Building new warehouse.
-
Buying a new machine.
-
Developing new product
-
Development or buying another company.
-
-
Evaluation of the project on expected Future cash flows and discounted to the present value NPV, using appropriate discount rate.
-
Rate of Return and payback period.
